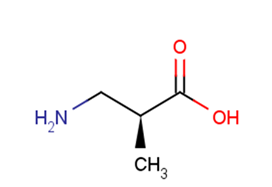
(S)-b-aminoisobutyric acid
CAS No. 4249-19-8
(S)-b-aminoisobutyric acid( —— )
Catalog No. M20747 CAS No. 4249-19-8
(S)-b-aminoisobutyric acid is a non-protein amino acid originating from the catabolism of thymine and valine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name(S)-b-aminoisobutyric acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description(S)-b-aminoisobutyric acid is a non-protein amino acid originating from the catabolism of thymine and valine.
-
Description(S)-b-aminoisobutyric acid is a non-protein amino acid originating from the catabolism of thymine and valine.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number4249-19-8
-
Formula Weight103.12
-
Molecular FormulaC4H9NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 250 mg/mL (2424.36 mM)
-
SMILESC[C@@H](CN)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Crumpler H R Dent C E Harris H et al. beta-Aminoisobutyric acid (alpha-methyl-beta-alanine); a new amino-acid obtained from human urine[J]. Nature 1951 167(4243):307-308.
molnova catalog



related products
-
N-Acetylhistamine
N-Acetylhistamine is a metabolite of histamine.
-
5-Methylcytidine
5-Methylcytidine is a modified nucleoside derived from 5-methylcytosine and is a minor constituent of RNA as well as DNA for certain organisms.
-
N-Lactoyl-Phenylalan...
N-Lactoyl-Phenylalanine (Lac-Phe) is a peptide coupling of lactic acid and phenylalanine, one of the metabolites in acute exercise, which can be used in the study of obesity and metabolism-related diseases.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


